
What does it involve?
Large Language Models (LLM) is a term that has gained great popularity with the development of OpenAI’s artificial intelligence-based ChatGPT. The term refers to specially adapted large-scale language models like GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3). These are machine learning models that can perform tasks using natural language processing (NLP). The models are trained on very large text datasets to gain the ability to generate text and understand linguistic context.
The transformer architecture contributes to the development of language model learning. This transformer architecture is based on the concept of attention, which enables the model to weigh up the meaning of different words in a specific context. This is achieved through a series of interrelated layers of attention that help the model to capture long-range relationships in the input text.
LLM is built on the encoder-decoder principle used in many neural machine translation models (neural machine translation or automatic text translation).
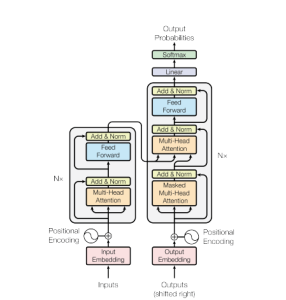
The concept of transformational architecture first appeared in 2017 in the article Attention Is All You Need.
Huge datasets
Language models are trained on huge data sets and then use different techniques to understand the relationships between words. Based on these relationships, they are able to generate new content. Such models are used in natural language processing (NLP) applications where users enter natural language queries. The more data we provide to train the models, the greater their capabilities will become.
There is no figure for what the minimum data needed for training is, but the LLM usually contains at least one billion parameters. The parameters are all the variables that are used by a model and from which a model inferences and generates information.
How does it work?
Creating a large language model is difficult and complicated, as well as expensive, so few companies can afford it. Often such an option remains beyond the reach of many companies. Ensuring that the LLM is highly effective requires that the model is trained on voluminous and properly prepared datasets. The model learns from the data provided to it, such as by using a dataset available on the internet.
The input data is fed into the model and is then subjected to a process known as unsupervised learning, meaning that human intervention in the learning process is minimal. The model is therefore not given any instructions on how to treat and use the data, which makes the model go into detail about the input data, the relationships and the relationships that exist between the data. After such a process, the model can guess, for example, the endings of phrases, sentences or create entire texts on a given topic, formulating answers to the questions asked. After the unsupervised learning phase, a fine-tuning phase of the model follows (fine-tuning process) on a smaller task-specific dataset. This process allows the model to adapt its skills and its knowledge to specific tasks, making it more effective.
The model then moves into the deep learning phase, using a transformer architecture. This allows the model to understand the relationships between the words and concepts, and teaches it to recognise them using a self-learning mechanism. Once all these phases are completed, the model is ready for practical use.

A powerful tool for the future?
Custom LLM – The Future of Natural Language Processing
Custom LLM is a technology that enables the creation and training of custom large-scale language models that are capable of automatic understanding (natural language understanding), human language generation (natural language generation) and interacting with it. The main technique used to train these models is machine learning, which also uses huge text datasets to teach the model to understand the semantics and structures of the language.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has undergone a real revolution in recent years with the introduction of non-standard large language models. These models, known as Custom Large Language Models, are somewhat of a breakthrough in the field of artificial intelligence, enabling the adaptation and use of vast amounts of textual data in innovative ways.
Custom large language models are an extension of generic language models, such as GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3) or BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), which are internationally known.
Custom LLMs go further than generic models, however, as they allow users to tailor them to specific needs. This means that these custom large language models work on specialised data to perform better in specific domains, generate content with a specific style or perform specific tasks in natural language processing.
There are various aspects that can be customised in such a large language model, including:
- Fine-tuning: Such models can be adapted by transforming them for a specific task. For example, a generic model can be trained to work better in a specific field, such as medicine, law or finance.
- Adding specialised data: Customisation also involves providing the model with specialised domain-specific training data to enhance its knowledge in that domain (adding data containing specialised terminology or industry specific terminology).
- Content limitations: Models can be adapted to release more specific or safer content, eliminating the generation of inappropriate or dangerous content.
- Different languages: The custom large language model’s performance can be customised to support multiple languages or dialects.
- Control of the style of the generated text: Customisation can include control over the style of the text being generated, such as to ensure that the text is more formal or more informal, as required.
These models have found applications in various fields, such as content generation, automatic translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots and many others. Due to their flexibility, CLLMs can be adapted to a wide range of applications and are an essential tool in the field of natural language processing.
Where can an LLM be applied?
Examples of the use of an LLM vary, ranging from content generation, data analysis, document production, IT coding and translation into foreign languages.
The possibilities for the use of LLMs are almost limitless and extremely varied.
- LMM can be used to generate content, articles, create slogans, including slogans in different languages, etc. Companies and content creators use custom models to create content for their websites, blogs, social media and other platforms. The models are also used as a tool to support the creative and design processes, while marketers use them extensively to generate ideas, supplement content or devise marketing strategies.
- They can be used as an internet search engine – answering the questions that the users ask.
- LLM also have a place in machine translation, where the models can be adapted to translate text from one language to another, facilitating communication between cultures and nations.
- Virtual assistant and chatbots are other functions that the language model can take over. Chatbots based on customised models are more flexible and can serve customers on websites, providing quick and relevant answers.
- The GPT chat is even able to write IT code, it can be used for programming, using data that has been processed in the past, allowing the model to create, for example, a computer programme.
- These models can be used in education to help create learning resources, generate questions and answers for quizzes and in language teaching.
- Custom Large Language Models help companies monitor public opinion on their products and services by analysing millions of reviews and comments. In business, these models can be used as tools for making personalised recommendations to customers, generating text in various fields, such as journalism or advertising, or for data analysis.
Advantages and disadvantages of LLM
The models can bring many benefits to companies and individual users. They can be tailored to specific needs, and additional training allows models to be created that are ideally suited to different applications, developed specifically for a given user or a given company or industry. One LLM can be used in many different cases, making it flexible and versatile.
These new language models are fast and efficient, and those that are trained on large amounts of data are also accurate and precise.
Large language models also have many disadvantages and limitations, which should also be mentioned. Among the biggest limitations is the lack of a full understanding of the context, and the models are not always able to understand context in the same way as humans. This is because they rely on statistics rather than human reasoning.
Language models often generate ‘hallucinations’, i.e. false or spurious results. They do not understand the content, or they just generate answers based on the data that has been provided for the training. Responses are generated based on the probability of words occurring in a particular order. LMMs may therefore introduce errors related to missing information in the training dataset. In simple terms, these models can only generate content similar to that on which they have been trained, meaning that they are not able to draw independent conclusions or generate information beyond their data scope.
Another very significant disadvantage of language models is the high cost of creating and maintaining them.
Ethics
Although Large Language Models bring many benefits, they also come with ethical and safety challenges. There is a risk that these models could be abused by using them to spread disinformation, generate inappropriate content or violate privacy.
Many people see LMMs as a threat and look to the future with trepidation, wondering when artificial intelligence will take over human jobs. Rather than seeing LLMs as a threat to our jobs, we can also see them as an aid, a support for our work. In this way, LLMs can change the way people do their work.
Summary
The rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) is fostering the emergence of new language models and the refinement of existing ones.
Large language models have both advantages and disadvantages. They are able to effectively support scientific activities, solving a variety of natural language processing tasks. They also support creative activities by generating a variety of content. On the other hand, these models still have many limitations and, despite continuous development, their performance is not flawless. They have enormous potential and, if the user is aware of these limitations, they are able to exploit the operation of the LMM in many areas. However, as this technology develops, it is important to simultaneously consider the ethical and safety issues to ensure that Custom Large Language Models are used appropriately.

